Managing multiple worksheets in Excel can be challenging, especially if you need to create a summary of their names. Instead of manually typing each worksheet name, you can automate the process with a VBA macro.
In This post i will show you how to use a simple VBA script to automatically list the names of all worksheets in your Excel workbook, excluding a specific sheet (e.g., “MasterSheet”).
Introduction to the VBA Macro
This VBA code automatically lists all the worksheet names in your workbook into a specified sheet, except for the sheet named “MasterSheet.” The macro scans through all the worksheets, identifies their names, and places them in a specified column in “MasterSheet.”
To set this up:
- Open your Excel workbook.
- Press
Alt + F11to open the VBA editor. - Insert a module by clicking
Insert > Module. - Paste the VBA code into the module.
Breaking Down the Code (Line-by-Line)
Option Explicit
This line ensures that all variables must be declared before they are used. It helps in catching errors caused by undefined variables.
Sub Button1_Click()
This begins the macro that will run when a button (such as a command button) is clicked. The macro will automate the process of listing all worksheet names.
Dim total_Sheets As Integer
Dim a As Integer
Two variables are declared here:
total_Sheets: Stores the total number of worksheets in the workbook.a: Used as a counter for the loop that will iterate through the worksheets.
total_Sheets = Worksheets.Count
This line assigns the total number of worksheets in the workbook to the total_Sheets variable. Worksheets.Count returns the number of sheets available.
For a = 1 To total_Sheets
This starts a loop that goes through each worksheet in the workbook. The variable a represents the index of the current worksheet.
If Worksheets(a).Name <> "MasterSheet" Then
This condition checks whether the current worksheet is not named “MasterSheet.” If it is named “MasterSheet,” the macro will skip it. This ensures that the “MasterSheet” is not listed in the result.
Worksheets("MasterSheet").Cells(a, 3).Value = Worksheets(a).Name
This line copies the name of the current worksheet to column C in “MasterSheet.” The variable a determines which row the name will be written in, creating a list of worksheet names starting from row 1 in column C.
Next a
End Sub
The Next a line moves the loop to the next worksheet, repeating the process until all worksheets have been processed. The End Sub marks the end of the macro.
Full Code Example
Here is the complete code that you can use in your workbook:
Option Explicit
Sub Button1_Click()
Dim total_Sheets As Integer
Dim a As Integer
total_Sheets = Worksheets.Count
For a = 1 To total_Sheets
If Worksheets(a).Name <> "MasterSheet" Then
Worksheets("MasterSheet").Cells(a, 3).Value = Worksheets(a).Name
End If
Next a
End Sub
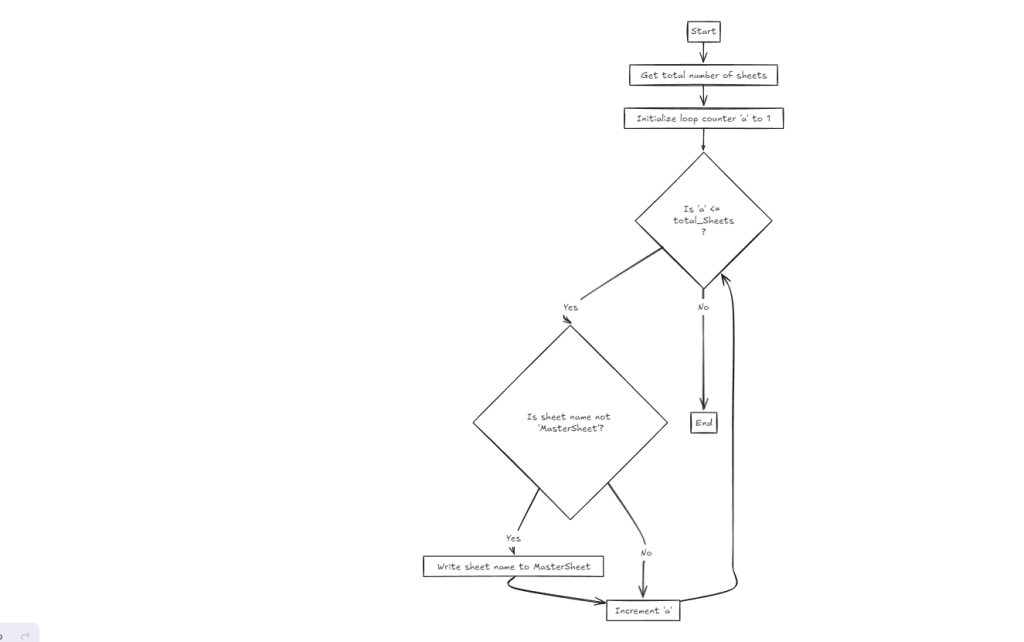
Flow Chart of the code
Running the Code
To run the macro:
- Press
Alt + F8in Excel. - Select
Button1_Click. - Click
Run.
Alternatively, you can assign this macro to a button (such as a command button) on your worksheet. This way, whenever you click the button, the macro will automatically list the worksheet names in “MasterSheet.”
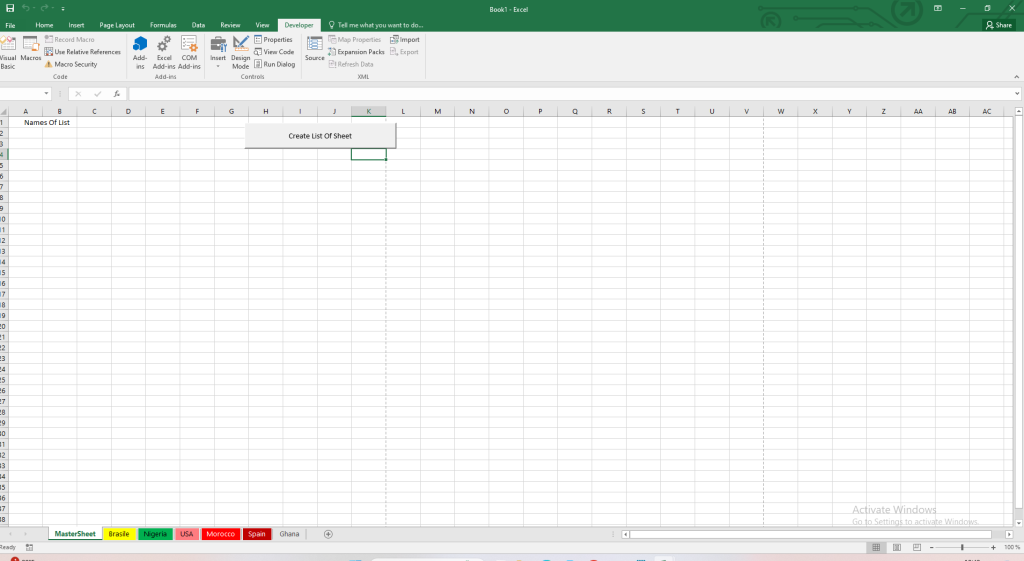
Result
Before
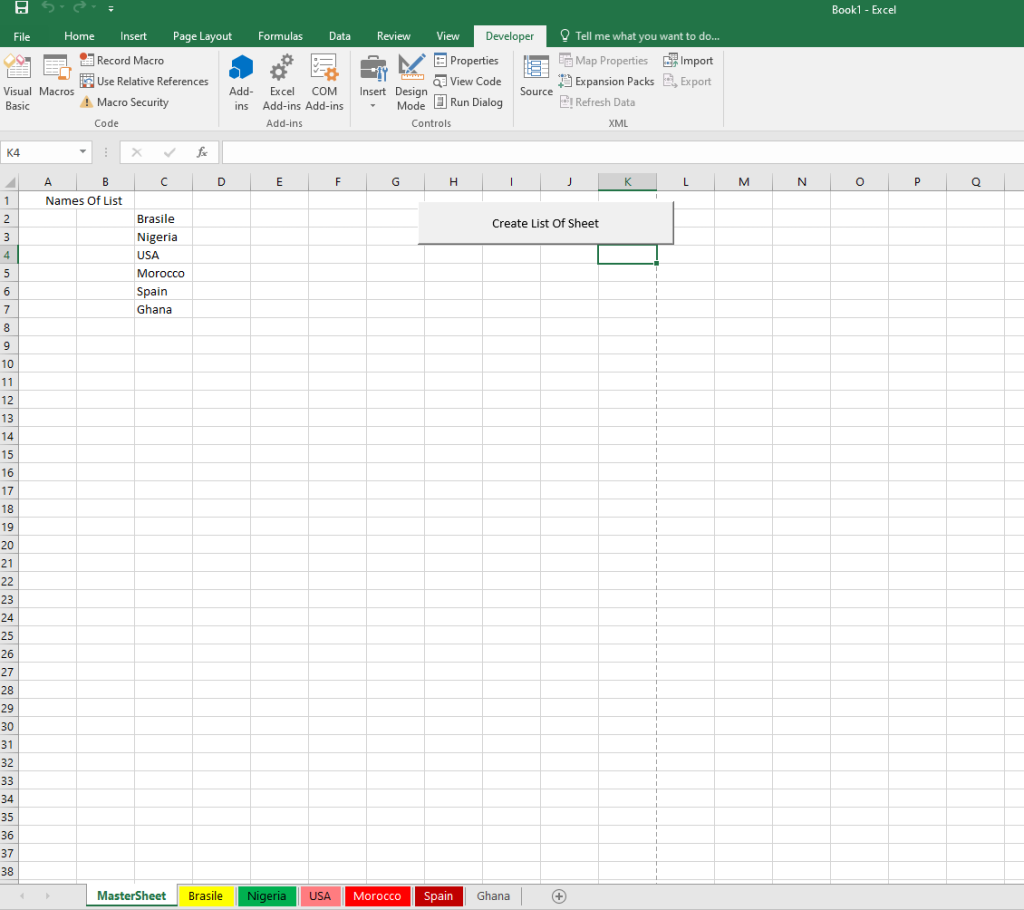
After
After running the macro, the “MasterSheet” will have a list of all the other worksheet names in column C. Each worksheet’s name will appear in a separate row, starting from row 1.
Conclusion
Using VBA, you can quickly generate a list of worksheet names in Excel, saving time and reducing the risk of manual errors. This method is useful when managing multiple sheets and needing an overview of the workbook’s structure.
Resources
For more information about using VBA in Excel, visit Microsoft’s official VBA documentation. and Pillow
if you like this blog post on How to List Worksheet Names in Excel Automatically Using VBA, then you would love our other blog post on How to Copy Excel Files Between Folders Using VBA in Excel